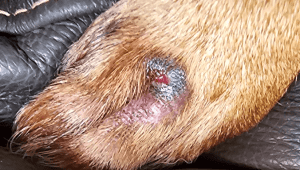
Dog Abscess: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention Guide
Discover everything about dog abscesses—painful bacterial lumps caused by infections. Learn key symptoms, risks, and essential care steps for quick recovery.
Have you ever noticed a painful, swollen lump on your furry friend? It might be a dog abscess, a common yet potentially serious condition that affects many canines. We’ll explore what dog abscesses are, their causes, and why prompt attention is crucial for your pet’s health.
Dog abscesses are pockets of pus that can develop anywhere on a dog’s body, from just under the skin to internal organs. They’re often caused by bacterial infections resulting from puncture wounds or other injuries. While skin abscesses are the most common, these painful swellings can also occur in anal glands, teeth roots, and even vital organs like the liver or brain. Understanding the signs and risks of abscesses is essential for every dog owner to ensure their pet’s well-being.
What Is a Dog Abscess?
A dog abscess is a localized collection of pus that forms beneath the skin or within body tissues. It’s typically caused by a bacterial infection, often resulting from puncture wounds, bites, or other injuries. Abscesses can develop in various parts of a dog’s body, including:
- Under the skin
- In anal glands
- Around tooth roots
- Internal organs (e.g., liver, brain)
The formation of an abscess is the body’s attempt to wall off an infection. As the immune system fights the invading bacteria, white blood cells accumulate, creating a pocket of pus. This process leads to swelling, inflammation, and pain in the affected area.
Characteristics of dog abscesses include:
- Swelling: A noticeable lump or bump on the body
- Heat: The affected area feels warm to the touch
- Pain: Dogs may show discomfort when the area is touched
- Redness: Inflammation causes the surrounding skin to appear red
- Discharge: If the abscess ruptures, it may release pus and blood
It’s crucial to recognize that abscesses can occur both externally and internally. While skin abscesses are more common and easily noticeable, internal abscesses in organs like the liver or brain can be more challenging to detect and potentially more dangerous.
Causes of dog abscesses include:
- Puncture wounds from fights with other animals
- Embedded foreign objects (e.g., grass seeds, splinters)
- Dental infections
- Anal gland impactions
- Insect bites or stings
- Post-surgical complications
Left untreated, a dog abscess can lead to more severe complications, including:
- Chronic infection
- Spread of infection to other body parts
- Sepsis (a life-threatening systemic infection)
Prompt veterinary attention is essential when a dog develops an abscess. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and ensure a faster recovery for the affected dog.
Common Causes of Abscesses in Dogs
Abscesses in dogs can develop from various sources, often resulting from bacterial infections. Understanding these common causes helps pet owners identify potential risks and seek prompt veterinary care when needed.
Bite Wounds and Injuries
Bite wounds and injuries are frequent culprits in abscess formation in dogs. These incidents compromise the skin barrier, allowing bacteria to enter and multiply:
- Puncture wounds from animal bites or sharp objects create ideal entry points for bacteria
- Scratches from other animals or environmental hazards can lead to infections
- Foreign objects like sticks, grass seeds, or needles can penetrate the skin and introduce bacteria
- Insect bites, particularly from ticks and mosquitoes, may cause localized infections
- Skin allergies resulting in excessive licking or chewing can create hot spots, a type of surface abscess
Active dogs face a higher risk of encountering potentially harmful objects or situations that could lead to abscess-causing injuries.
Dental Issues
Dental problems are a important contributor to abscess formation in dogs, particularly in the oral cavity:
- Dental abscesses often develop due to infections at the root of a tooth
- Tartar accumulation and gingival inflammation increase the risk of dental abscesses
- Fractured or damaged teeth provide entry points for bacteria
- Poor oral hygiene can lead to bacterial overgrowth and subsequent infections
- Periodontal disease, if left untreated, may progress to abscess formation
Regular dental check-ups and proper oral care are crucial in preventing dental-related abscesses in dogs.
Anal Gland Problems
Anal gland issues can lead to abscess formation in dogs, causing discomfort and potential complications:
- Impacted anal glands can become infected, leading to abscess development
- Anal gland abscesses often result from blockages preventing normal secretion
- Bacterial overgrowth in the anal sacs can contribute to infection and abscess formation
- Dogs with chronic anal gland problems are at higher risk of developing abscesses
- Certain breeds, particularly small breeds, are more prone to anal gland issues
Regular anal gland expression and proper hygiene can help prevent anal gland abscesses in susceptible dogs.

Signs and Symptoms of Dog Abscesses
Dog abscesses present various signs and symptoms depending on their location and severity. Recognizing these indicators is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment.
General Symptoms
Dog abscesses typically exhibit several common symptoms:
- Swelling and redness: A noticeable lump or swollen area, often warm to the touch
- Pain and discomfort: Dogs may lick, bite, or chew the affected area
- Hair loss: Fur may thin or fall out around the abscess site
- Pus and discharge: Rupturing abscesses release a foul-smelling fluid
- Systemic symptoms: Fever, reduced appetite, lethargy, or vomiting in severe cases
These signs can vary in intensity, but any combination should prompt immediate veterinary attention to prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
Exact Symptoms by Location
Abscesses in different parts of a dog’s body present unique symptoms:
- Skin abscesses:
- Visible lumps under the skin
- Redness and warmth in the affected area
- Localized hair loss
- Constant licking or biting of the site
2. Dental abscesses:
- Swelling below the eye
- Bad breath and drooling
- Chewing on one side of the mouth
- Reluctance to eat or be touched on the face
3. Anal gland abscesses:
- Pain and swelling around the anus
- Scooting or rubbing bottom on the ground
- Excessive biting and hair loss around the rear
- Straining during defecation
4. Internal abscesses:
- Difficulty urinating or defecating
- Blood in urine
- Abdominal pain
- Reluctance to walk or move
Recognizing these location-exact symptoms helps pinpoint the abscess type, enabling faster diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Diagnosis of Dog Abscesses
Diagnosing dog abscesses involves a comprehensive approach combining physical examination, clinical symptoms assessment, and additional diagnostic tests. Veterinarians use various methods to accurately identify and evaluate abscesses in dogs.
Physical Examination and Clinical Symptoms
Physical examination is the primary tool for diagnosing dog abscesses. Vets look for:
- Swelling: Localized areas of inflammation
- Redness: Discoloration of the affected area
- Warmth: Increased temperature in the abscess region
- Pain: Discomfort when the area is touched
- Licking or biting: Dog’s attention to the affected area
- Hair loss: Thinning or absence of fur around the abscess
For skin abscesses, vets palpate the area to feel for soft or firm lumps. The abscess site often feels warmer than surrounding skin. Internal or body cavity abscesses may present with:
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Reduced appetite
- Exact signs based on location (e.g., scooting for anal gland abscesses, reluctance to eat for tooth abscesses)
Diagnostic Tests
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause, vets may employ several diagnostic tests:
- Blood tests: Assess overall health and detect signs of infection
- Microscopic examination: Analyze fluid from the abscess
- Bacterial culture: Identify the exact bacteria causing the infection
- X-rays: Detect internal abscesses or foreign objects
- Ultrasound: Visualize internal abscesses and surrounding tissues
- Surgical biopsies: Obtain tissue samples for detailed analysis
For challenging cases, especially internal abscesses, vets may use a combination of these advanced diagnostic methods.
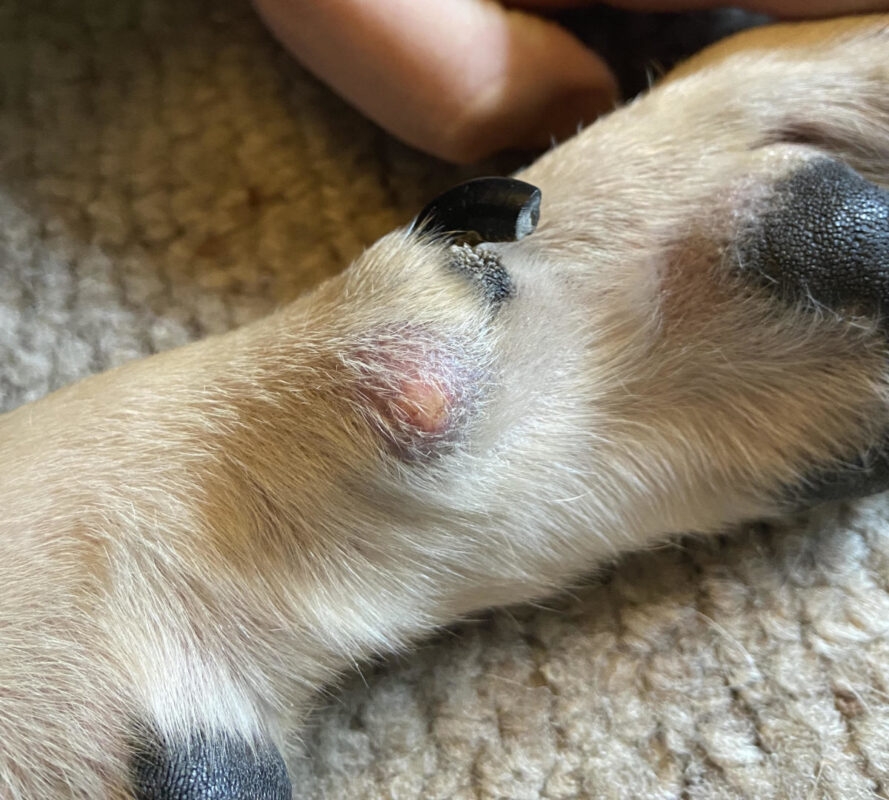
Exact Diagnostic Approaches
Different types of abscesses require customized diagnostic approaches:
- Skin abscesses:
- Visual inspection
- Palpation
- Needle aspiration for fluid analysis
2. Dental abscesses:
- Oral examination
- Dental X-rays
- Probing of gum pockets
3. Anal gland abscesses:
- Rectal examination
- Palpation of anal glands
- Evaluation of anal gland secretions
4. Internal abscesses:
- Comprehensive blood tests
- Urinalysis
- Imaging studies (X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans)
Diagnostic Challenges
Certain factors can complicate the diagnosis of dog abscesses:
- Deep-seated abscesses: May not show obvious external signs
- Multiple abscesses: Can mask individual characteristics
- Chronic abscesses: May have atypical presentations
- Breed-exact factors: Some breeds (e.g., Labradors, English Bulldogs) are more prone to certain types of abscesses
In these cases, vets may need to employ a combination of diagnostic techniques for accurate assessment.
Importance of Prompt Diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis of dog abscesses is crucial for:
- Preventing spread of infection
- Minimizing pain and discomfort
- Avoiding complications like sepsis
- Determining appropriate treatment plans
- Ensuring faster recovery
By utilizing a comprehensive diagnostic approach, veterinarians can effectively identify and treat dog abscesses, promoting better health outcomes for affected pets.
Treatment Options for Dog Abscesses
Dog abscesses require prompt and effective treatment to prevent complications and alleviate discomfort. Treatment options typically involve a combination of veterinary care and home management strategies.
Veterinary Treatment
Veterinary treatment for dog abscesses involves a comprehensive approach to diagnose, drain, and treat the infection. The diagnosis typically begins with a physical examination, which may be supplemented by diagnostic tools such as fine needle aspirates, blood tests, and bacterial cultures. Once diagnosed, the primary treatment involves draining the abscess. This procedure is usually performed under sedation or anesthesia to minimize pain. The veterinarian will clip the hair around the swelling, disinfect the area, and lance the abscess to drain the pus. After draining, the abscess is flushed with saline or another tissue-friendly solution to clean out the infected pocket. Antibiotic therapy is a crucial component of treatment, with oral antibiotics commonly prescribed to combat the bacterial infection.
Home Care and Management
While veterinary treatment is essential for dog abscesses, proper home care and management play a vital role in the recovery process. Once your dog has received appropriate medication from the veterinarian, there are several steps you can take to support their healing:
- Medication adherence: Administer prescribed medications as directed, ensuring you complete the full course of antibiotics.
- Wound care: If recommended by your vet, clean the open abscess with saline solution.
- Rest and comfort: Provide a quiet, comfortable space for your dog to rest, limiting exercise during treatment.
- Diet management: Ensure your dog maintains a good appetite, offering soft or highly palatable food if necessary.
- Monitoring: Observe your dog closely for any changes in the abscess or overall condition.
- Follow-up care: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your veterinarian.
It’s important to note that most abscesses require professional veterinary care and shouldn’t be treated solely at home. Home care should complement, not replace, veterinary treatment. If you notice any signs of systemic infection, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or fever, seek immediate veterinary attention.
Potential Complications of Untreated Abscesses
Untreated dog abscesses can lead to severe complications, affecting the overall health and well-being of our canine companions. We’ll explore some of the most common and serious potential outcomes of neglecting these infections.
Systemic Infection
When a dog abscess remains untreated, bacteria can spread through the bloodstream, causing systemic infection. This condition, known as sepsis, can be life-threatening. Signs of systemic infection include:
- Lethargy
- Loss of appetite (hyporexia)
- Vomiting
- Elevated body temperature
For example, in hepatic abscesses, bacteria like Escherichia coli can enter the bloodstream, leading to these severe symptoms. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent the infection from spreading and causing widespread organ damage.
Neurologic Dysfunction
Spinal abscesses pose a important risk to a dog’s nervous system. If left untreated, they can cause severe neurologic deficits due to spinal cord compression. Symptoms of neurologic dysfunction include:
- Acute spinal pain
- Paraparesis (partial paralysis of the hind limbs)
- Paraplegia (complete paralysis of the hind limbs)
- Lethargy
- Anorexia
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are essential to prevent permanent neurologic damage. These complications can severely impact a dog’s quality of life and may lead to long-term mobility issues.
Organ Dysfunction
Abscesses in vital organs, such as the liver, can cause important organ dysfunction if not addressed promptly. In the case of hepatic abscesses, we may observe:
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Hypoalbuminemia (low blood albumin levels)
- Hyperbilirubinemia (high blood bilirubin levels)
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
These symptoms indicate liver dysfunction and can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Regular veterinary check-ups and prompt attention to any signs of illness can help prevent these complications.
Chronic Pain and Discomfort
Untreated abscesses can cause persistent pain and discomfort for dogs. This chronic condition can lead to:
- Decreased activity levels
- Altered behavior
- Reduced quality of life
Addressing abscesses early can prevent long-term suffering and ensure our canine companions maintain their usual happy and active lifestyles.
Spread of Infection to Surrounding Tissues
When dog abscesses are left untreated, the infection can spread to nearby tissues and organs. This spread can result in:
- Larger, more complex abscesses
- Multiple abscesses in different locations
- Involvement of deeper tissues or adjacent organs
Treating abscesses promptly helps contain the infection and prevents it from affecting a wider area of the body.
Delayed Healing and Scarring
Untreated abscesses can lead to prolonged healing times and extensive scarring. This can result in:
- Permanent hair loss at the abscess site
- Skin discoloration
- Tissue damage and deformity
Early intervention and proper treatment can minimize scarring and promote faster healing, preserving the dog’s skin and coat integrity.
Compromised Immune System
Chronic, untreated abscesses can weaken a dog’s immune system, making them more susceptible to other infections and diseases. This compromised immunity can lead to:
- Increased vulnerability to opportunistic infections
- Slower recovery from illnesses
- Overall decreased health and vitality
Maintaining a strong immune system is crucial for a dog’s long-term health, and addressing abscesses promptly plays a important role in this.
By understanding these potential complications, we can better appreciate the importance of early detection and treatment of dog abscesses. Regular veterinary check-ups, prompt attention to any signs of illness, and proper home care are essential in preventing these serious outcomes and ensuring our furry friends lead healthy, happy lives.
Preventing Abscesses in Dogs
Preventing abscesses in dogs requires a proactive approach to their health and well-being. While not all abscesses are preventable, we can take several measures to minimize the risk of these painful infections.
Identifying and Managing Risk Factors
Understanding the common causes of abscesses helps us take preventive action. Here are key risk factors and prevention strategies:
Foreign Bodies
Foreign bodies, such as sticks, grass, or plant material, can penetrate a dog’s oral mucosa and migrate into the neck, causing cervical abscesses. To reduce this risk:
- Discourage dogs from chewing on sticks or foreign objects
- Provide safe, appropriate chew toys
- Regularly inspect your dog’s mouth for any signs of injury or embedded objects
Trauma
Oropharyngeal trauma can lead to abscess formation. To minimize this risk:
- Supervise dogs during play to prevent injuries
- Avoid rough play that could cause cuts or punctures
- Promptly clean and disinfect any wounds from fights or bites
Infections
Bacterial infections are a primary cause of abscesses. To prevent these:
- Keep your dog’s vaccinations up to date
- Maintain good hygiene practices, including regular bathing and grooming
- Address any skin irritations or injuries promptly
Dental Care and Hygiene
Proper dental care is crucial in preventing dental abscesses:
- Brush your dog’s teeth regularly with dog-friendly toothpaste
- Provide dental chews and toys designed to promote oral health
- Schedule professional dental cleanings with your veterinarian at least every 6 months
- Use special dental food if recommended by your vet
Wound Care and Management
Proper wound care can prevent abscesses from forming:
- Clean any cuts, scratches, or bites immediately with an antiseptic solution
- Keep wounds clean and dry
- Monitor healing progress and seek veterinary care if signs of infection appear
Environmental Precautions
Taking environmental precautions can reduce the risk of abscesses:
- Avoid areas with grass seeds during summer months
- Check your dog thoroughly after walks, especially between toes and in ears
- Remove any grass seeds or foreign objects from your dog’s coat promptly
- Keep your yard free of hazardous objects that could cause puncture wounds
Regular Health Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for preventing and detecting potential abscess-causing conditions:
- Schedule routine health examinations at least twice a year
- Address any health concerns promptly
- Keep up with recommended vaccinations and preventive treatments
Anal Gland Care
Proper anal gland care can prevent anal gland abscesses:
- Learn to recognize signs of anal gland problems, such as scooting or excessive licking
- Consider adding fiber supplements to your dog’s diet if recommended by your vet
- Have your dog’s anal glands checked and expressed regularly if they’re prone to issues
Neutering
For male dogs, neutering can help prevent prostate abscesses:
- Discuss the benefits of neutering with your veterinarian
- Consider neutering at an appropriate age to reduce the risk of prostate issues
First Aid Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies can help prevent minor injuries from developing into abscesses:
- Keep a pet first aid kit stocked with essentials like tweezers and sterile saline
- Learn basic wound cleaning techniques
- Know when to seek professional veterinary care
By implementing these preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the risk of abscesses in dogs. While it’s impossible to prevent all abscesses, a proactive approach to your dog’s health and safety can go a long way in minimizing their occurrence and ensuring your pet’s overall well-being.
When to Seek Emergency Veterinary Care
Recognizing when a dog abscess requires immediate medical attention is crucial for preventing severe complications. We’ll outline exact scenarios that necessitate emergency veterinary care for dog abscesses.
Systemic Infection Signs
Systemic infection symptoms indicate a need for urgent veterinary attention:
- Lethargy or listlessness
- Loss of appetite
- Fever (temperature above 103°F or 39.4°C)
- Severe pain or discomfort
These signs suggest the infection has spread beyond the abscess site, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
Abscess Location Concerns
Certain abscess locations pose higher risks and require immediate veterinary care:
- Near the eyes
- Around the ears
- In the genital area
- Close to the anus
Abscesses in these areas can quickly spread to vital organs or cause severe complications if left untreated.
Healing Complications
Seek veterinary attention if:
- The abscess doesn’t show signs of healing within 2-3 days of home treatment
- The area around the abscess becomes increasingly swollen or painful
- There’s a foul odor emanating from the abscess
- The discharge changes color or consistency
These signs may indicate antibiotic resistance or the presence of a foreign object in the wound.
Neurological Symptoms
For potential spinal abscesses, watch for:
- Acute paraparesis (partial paralysis of the hind limbs)
- Paraplegia (complete paralysis of the hind limbs)
- Spinal pain
- Abnormal gait or difficulty walking
These symptoms require immediate veterinary evaluation to prevent permanent neurological damage.
Liver Abscess Indicators
Signs that may indicate a liver abscess include:
- Persistent vomiting
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin, gums, or eyes)
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Dark urine or pale stools
Liver abscesses can lead to organ dysfunction and require prompt medical intervention.
Retrobulbar Abscess Signs
For abscesses behind the eye, look out for:
- Protrusion of the eye
- Swelling around the eye area
- Discharge from the eye
- Difficulty opening the eye or keeping it open
These symptoms can indicate a retrobulbar abscess, which needs immediate attention to prevent vision loss.
Ruptured Abscess Management
If an abscess ruptures:
- Keep the area clean to prevent further contamination
- Don’t allow the wound to close prematurely
- Avoid covering the area with bandages that prevent drainage
While drainage is beneficial, a ruptured abscess still requires veterinary care to ensure proper healing and prevent infection spread.
Blood Test Abnormalities
Consider emergency care if blood tests reveal:
- Neutrophilia (elevated white blood cell count)
- Toxic changes in blood cells
- Anemia
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
- Elevated liver enzymes
These abnormalities can indicate a severe systemic infection requiring immediate treatment.
By understanding these critical signs, we can ensure timely veterinary intervention for dog abscesses, significantly improving the chances of a full recovery and preventing potentially life-threatening complications.
Conclusion
Dog abscesses require prompt attention and proper care. We’ve explored their causes symptoms diagnosis and treatment highlighting the importance of early intervention. By understanding preventive measures and recognizing warning signs pet owners can safeguard their dogs’ health. Remember that professional veterinary care is crucial for managing abscesses effectively. Stay vigilant monitor your pet’s health and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed. With the right approach we can ensure our furry companions lead happy healthy lives free from the discomfort of abscesses.